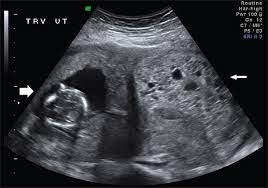
The complicated medical condition known as intrauterine pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg is placed within the uterus and begins to grow there. Pregnancy can only be sustained when it occurs inside the uterus. Ectopic pregnancy is the word used to describe a pregnancy that occurs any place else in the female reproductive tract, such as the cervix, fallopian tubes, or ovary.
They frequently result in abortion or miscarriage and are brief in nature. The baby is too little to notice when an early intrauterine gestational sac forms within the womb during an early intrauterine pregnancy. Allow us to enlighten you on some fundamental facts regarding intrauterine pregnancy, such as whether it is harmful or normal. Let’s find out intra uterine, single viable intrauterine pregnancy meaning if early intrauterine pregnancy is good or bad.
What Is the Procedure For Confirming An IUP?
An intrauterine pregnancy can be confirmed by the tests listed below. Nonetheless, the most popular method for determining the location of a pregnancy is an ultrasound scan.
Visible Yolk Sac
Let’s talk about what a single intrauterine gestational sac means. At 5.5 weeks of pregnancy, an ultrasound shows the presence of a yolk sac. Ultrasonography can confirm an intrauterine pregnancy when an embryo grows and becomes visible.
Also Read : How to Fake a Pregnancy Test : Tips and Tricks
Fetal Heart Activity
Fetal heart activity is visible six weeks into the pregnancy. The fetus’s heart rate rises weekly, averaging between 100 and 120 beats per minute.
Intrauterine Pregnancy
When a fertilized egg descends the fallopian tube and implants in the lining of your uterus, it is known as an intrauterine pregnancy. From an embryo to a fetus and, eventually, a newborn, it grows and develops here.
It’s ectopic if the pregnancy is not inside your uterus. The American Society for Reproductive Medicine estimates that 1-2 per cent of conceptions result in an ectopic pregnancy.
Ectopic pregnancies cannot survive. If a pregnancy becomes ectopic, you will require emergency medical attention. The usual course of treatment for an ectopic pregnancy is medication or surgery. An ectopic pregnancy may burst if it advances too far and the embryo becomes too large. There can be severe internal bleeding, which makes this a medical emergency. More severe consequences can be avoided with early intervention.
Intrauterine pregnancy symptoms – double decidual sac sign
There are several indicators and symptoms of early pregnancy, such as: missing a monthly cycle; a positive pregnancy test; sore breasts or nipples; exhaustion; dietary aversions and desires; frequent urination; and mood swings.
The fact that your pregnancy is in your uterus and not ectopic is confirmed by none of the symptoms. The following are signs of an ectopic pregnancy to be aware of.
- double decidual sac
- • unexplained bleeding;
- • stomach or pelvic discomfort
- • low back pain
- • one side cramping
Types of Intrauterine Pregnancy
There are two major types of intrauterine pregnancy as follow.
Single live intrauterine pregnancy meaning
In obstetrics, this phrase describes a certain situation in which there is just one growing foetus within the uterus during pregnancy. It represents a single embryo that has successfully implanted into the uterus lining and is moving in the direction of a typical foetal development.
Compared to multiple gestations, this scenario is thought to be usual for the majority of pregnancies and is linked to a decreased risk of problems. From a clinical perspective, establishing a single viable intrauterine pregnancy is essential for prenatal care because it enables medical professionals to track the fetus’s growth and development precisely.
Also Read : Can I Eat Slim Jims while Pregnant? lets find out
Intrauterine gestation
The term “intrauterine gestation” describes a pregnancy that develops and progresses only inside the uterus. It includes every step of foetal development inside the typical anatomical region for gestation, from conception and implantation to birth.
This phrase is essential for differentiating between a pregnancy that is developing healthily inside the uterus and other possible situations, such as molar pregnancy or ectopic pregnancy, in which implantation takes place outside the uterine cavity or includes aberrant tissue growth. In obstetrics, intrauterine gestation is the ideal result as it symbolizes a normal and healthy pregnancy trajectory.
Early intrauterine pregnancy is good or bad?
When the fetus has a regular heartbeat and is visible in the proper location within the womb (the uterus), the intrauterine pregnancy is considered normal. If you’re farther along, it could be a sign that the pregnancy has unfortunately failed, although intrauterine pregnancy is a typical early pregnancy finding.
To determine the safety of the pregnancy, a second scan is often provided in 7–14 days. A low heart rate (less than 80 beats per minute) before to 6.3 weeks of pregnancy is linked to a poor prognosis and an increased risk of problems throughout the first trimester. Less than 100 bpm is linked to a greater chance of miscarriage, whereas 120 bpm is linked to an incorrect diagnosis between 6.3 and 7 weeks.
An intrauterine pregnancy can mean two things
An intrauterine pregnancy (IUP) may indicate two important things in obstetrics. First, it indicates a healthy, viable pregnancy in which the fertilised egg has settled in the uterus, which is the best place for the growth and development of the foetus. This situation, provided no further issues occur, lays the scene for a potentially good pregnant journey.
Second, it’s important to distinguish this phrase from ectopic pregnancy, which is a dangerous medical disease in which the embryo implants outside of the uterus, usually in the fallopian tubes.
Determining the presence of an intrauterine pregnancy is crucial for verifying both the gestational age and the existence of the pregnancy, as well as for ruling out an ectopic pregnancy and directing prompt and necessary medical care. This distinction highlights the significance of early prenatal testing and monitoring and is crucial for the management and prognosis of the pregnancy.
What are the Causes of Intrauterine Pregnancy?
Some of the main reasons for intrauterine pregnancy are listed below:
Abnormal Genes and Chromosomes
Abnormal genes, extra chromosomes, and consequent abnormalities in the DNA sequence are among the primary causes of miscarriages. This may cause the foetus to develop abnormally and improperly in the mother’s womb. It’s not always the case that these anomalies are inherited.
Such anomalies may arise in the embryo in the early stages of pregnancy. This mostly occurs throughout the embryo’s division and development phase.
A foetus that has severe chromosomal abnormalities may die in the pregnancy.
Poor or Compromised Maternal Wellbeing
Undiagnosed medical conditions in the mother may have contributed to previous miscarriages during intrauterine pregnancy. Among the main problems that might cause these kinds of miscarriages are:
Diabetes
One of the main illnesses that might cause issues during pregnancy is diabetes. Therefore, it is best to take the appropriate precautions for gestational diabetes to ensure that your health and the health of your unborn child are not jeopardised during the early stages of pregnancy.
Hormonal Imbalances
The uterus and its health are the most critical factors during intrauterine pregnancy. However, physiological problems like low pregnancy hormone levels can cause the uterine lining to shrink. This affects the uterus’s health, which makes egg implantation challenging. It also makes it difficult to understand how an embryo develops.
Serious Infections
Some types of illnesses, such as malaria, CMV, listeriosis, toxoplasmosis, syphilis, and HIV infections, can cause problems during intrauterine pregnancy.
Cervical Issues
When the cervix cannot support and nourish the developing embryo, the likelihood of miscarriage during an intrauterine pregnancy increases. It is unlikely that the pregnancy will end if you have fragile cervical concerns or an incompetent cervix.
Age
A safe pregnancy and subsequent birth are more likely to occur in women under 35. However, the likelihood of losing an intrauterine pregnancy is 20% higher in older women, defined as those over 35. At forty, the odds of miscarriage increase to forty per cent, and by forty-five, they have doubled to eighty per cent.
History of Miscarriages
Women who have previously experienced a miscarriage are more likely to experience one again. However, receiving the right care and attention might subsequently lower the likelihood of miscarriage. Thus, never give up and always seek the advice of a medical professional in such cases.
Substance Abuse
There are lifestyle choices that lower the likelihood of a successful intrauterine pregnancy, including drinking, smoking, and drug misuse. The uterine lining can be disrupted by all the carcinogens in drugs and tobacco, which makes it harder for the mother’s womb to contain the fetus.
Intrauterine Pregnancy Treatment to Avoid Complications
Here are some lifestyle factors to watch out for to prevent certain difficulties that might result in miscarriage or issues after birthing.
Make Healthy Dietary Choices
To maintain the health of your uterus, always remember to consume a nutritious, well-balanced, and healthful diet. Additionally, don’t forget to include antioxidants in your diet to boost your defences against illness and provide greater health for your unborn child. Because of their high nutritional content, leafy greens are a reliable choice for an intrauterine pregnancy that will last.
Quit Smoking
In addition to being bad for your health, smoking is a waste of time and energy that can have severe effects on a successful pregnancy. Give up and get the health benefits of stopping smoking, including the possibility of a long-term intrauterine pregnancy.
Get Treatment for APS
Antiphospholipid syndrome, or APS, is a disorder where women have a weak cervix that prevents the embryo from implanting and from feeding. As a result, be sure to receive the right care for this illness.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Keeping a healthy weight is another approach to avoiding all the problems associated with intrauterine pregnancy. Thus, before and after becoming pregnant, keep a healthy weight.
When to Consult a Doctor During Intrauterine Pregnancy?
If you are experiencing health issues, schedule an appointment with an OB/GYN. An intrauterine pregnancy failure may be indicated if you have brown spotting or sudden vaginal bleeding.
FAQs
How many weeks is early intrauterine pregnancy?
The first 12 weeks of pregnancy, often known as the first trimester, are usually called early intrauterine pregnancy.
How do you confirm intrauterine pregnancy?
Ultrasonography, which can see the gestational sac inside the uterus at about five weeks of gestation, is used to confirm intrauterine pregnancy. Moreover, increasing beta-hCG hormone levels confirm the diagnosis.
Can an Intrauterine Pregnancy Survive?
With the right care and monitoring, 50–60% of intrauterine pregnancies are said to survive.
Is Intrauterine Pregnancy a Normal Pregnancy?
when the foetus exhibits a regular heartbeat and the embryo is placed in the uterus at the proper location.
Is an Intrauterine Pregnancy a High-Risk Pregnancy?
Stillbirth is one of the biggest risk factors during intrauterine pregnancy, making it a high-risk pregnancy.
Last words: Early intrauterine pregnancy is good or bad?
What is intrauterine pregnancy? Or is intrauterine pregnancy bad? It’s a complicated ailment that requires ultrasonography diagnosis. In this blog we have talked about; single live intrauterine pregnancy meaning & all related details. To validate your doctor’s first concerns of an early intrauterine pregnancy, a follow-up screening is typically required. Remember that aberrant genes or chromosomes can raise the risk of intrauterine pregnancy failure, as might certain maternal health issues.
Also Read : How to Keep C-section Incision Dry When Overweight